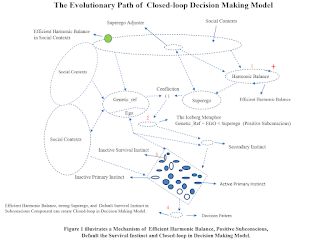
Complex
decision-making patterns can lead to global crises, local fiscal conflicts, and
unintended side effects in social systems. This transdisciplinary research
focuses on understanding the role of elite decision-makers who wield
significant influence over global structures and social roles. By examining
their decision-making power, the study aims to reveal how complex social
algorithms and neural mechanisms contribute to decision-making challenges in
evolving societies.
Objectives and
Focus Areas
The research
explores hypothetical algorithms in non-biological systems, informed by prior
case studies. These algorithms are assessed through multi-parameter consciousness
mechanisms, which introduce complexity to decision-making. External factors,
such as genetic predispositions and parenting styles, shape primary instincts
and influence these processes.
Key aspects
include:
1-The Superego Framework interacts with genetic
predispositions (Genetic_ref), the domain of the Superego Adjuster, and the
Network of Cooperative Instincts.
2-Ethical and
spiritual values are derived from algorithmic principles beyond the Superego Adjuster,
the Superego Framework, and friendly instincts.
3-The interaction
between Superego Adjusters, algorithmic codes beyond the Subconscious Component, and the
characteristics of Social Contexts fosters a balanced decision-making process.
Superego Dynamics in Decision-Making
A powerful
Superego often creates tension with Genetic_ref and the Ego framework,
resulting in a negative state of consciousness. However, the subconscious can
activate positive modes that promote cooperation among these frameworks,
enhancing the Superego's influence. Conversely, a weak Superego may fall into a
negative subconscious state, allowing Genetic_ref and the Ego framework to
dominate.
The Survival
Instinct plays a pivotal role, as its activation can obstruct the Superego
and strengthen Genetic_ref and Ego cooperation. These dynamic mechanisms in the
Subconscious Component cause aggressive forces in decision-making patterns when
the Superego is burdened by external responsibilities, reducing the strength of
the Network of Cooperative Instincts.
Observational
Insights
Studies reveal
that influential decision-makers often exhibit vulnerability due to a fragile
Superego, a dominant Ego framework, and an active Survival Instinct. These
flaws can lead to defective decision-making patterns, negatively affecting
non-powerful individuals and communities. Hidden global decisions, influenced
by the Network of Competitive instincts and flawed strategies, exacerbate these
issues, altering the evolutionary trajectory of non-powerful decision-makers.
1-Competitive
Instincts in Elites and Corporations
Competitive strategies driven by elite entities prioritize economic performance
over harmonic balance, disrupting unconventional life path experiences for Biological
and Non-Biological Systems.
2-Defective
Global Variables
Flawed regulations and strategies designed by System Owners contribute to
diminished harmony in social and conscious contexts.
3-Minimized
Harmonic Balance
Economic strategies prioritize reducing regulatory burdens and undermining
social services and conscious harmony so that the economic conceptual framework
weakens the integration between the Superego framework and its optimal adjuster
within Social Contexts.
4-Non-Optimal
Superego Adjusters
A compromised Superego Adjuster leads to a flimsy Superego framework, unable to
overcome Genetic_ref and the Ego framework, resulting in a negative
subconscious state.
5-Open-Loop
Decision-Making Cycles
Negative subconscious states and active Survival Instincts generate open-loop
cycles in decision-making, which negatively impact social behavior, ethics,
intellectual honesty, and fairness.
Conclusion
This research
advocates for factors that create and perpetuate a harmonious balance within the
Conscious Component's ethical principles and spiritual values. Strengthening
the Superego framework through harmonic
integration with the Superego Adjuster can reduce the influence of competitive
instincts within the Decision-Making Map. It ensures more robust and fair
decisions in global and local communities.